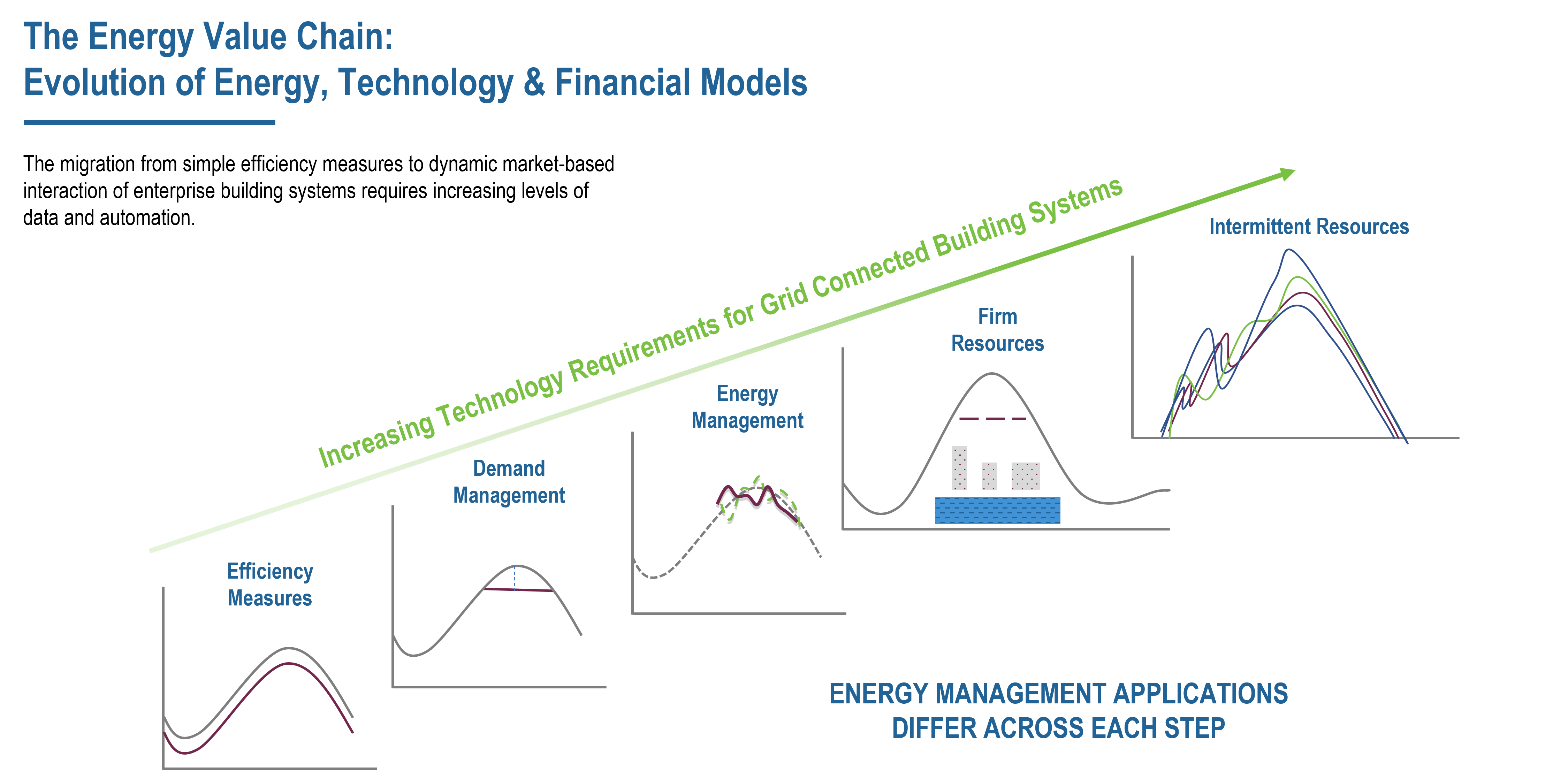
Demand Management Technologies and Modern Buildings
By: Leighton J. Wolffe
Energy markets across the United States continue to rapidly evolve due to regulatory, legislative and energy policy activity at the Federal, State, and regional levels. What has been a historically staid and slow-moving industry has now become supercharged with the advent of deregulation, renewable technologies, and distributed energy resources.
Large scale adoption of renewable energy resources such as solar, wind, storage, coupled with weather extremes and consumer demand are creating increasingly complex scenarios of supply, pricing, and risk. These factors drive the costs of electricity in unpredictable ways, requiring building owners to both understand the markets they reside in, and have ability to monitor, manage and effectively control energy usage. Moreover, they need the technologies necessary to participate in demand response and demand management programs.
In today’s new energy economy, buildings are intended to be part of an interactive energy grid – able to receive and respond to market signals that indicate that grid conditions are taking place due to critical issues with supply and demand. The grid operators now provide hour and day ahead pricing so that when prices are high, customers can elect to use less, or even nominate load back into the market and receive the same income as a power plant.
These new opportunities are being driven in large part by FERC Order 2222, which is specifically intended to open up markets to behind the meter distributed energy resources (DER’s). In summary, a customer can use less, or generate energy to offset what would normally be supplied from the grid and be paid for it.
FERC Order 2222 helps usher in the electric grid of the future and promote competition in electric markets by removing the barriers preventing distributed energy resources (DERs) from competing on a level playing field in the organized capacity, energy and ancillary services markets run by regional grid operators.
In addition, the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) executive order further incentivizes DER’s through tax credits. Under the IRA, energy transition projects undertaken by tax-exempt entities will qualify for the investment tax credit (ITC) equal to 30% to 70% of the eligible project cost basis. To put this simply, a qualifying project with an installed price of $1 million will now only cost $300,000 to $700,000 after factoring in the direct pay ITC.
Given the pace of FERC 2222, national and local activity, energy market models in place today will not stay the same as the regulated and competitive markets adjust to the increasing integration of grid scale renewables. This new mix of firm and intermittent energy resources directly impact the way energy suppliers price power purchasing agreements and how consumers pay for electricity originating from traditional and renewable energy sources.
US Deregulated Energy Markets:
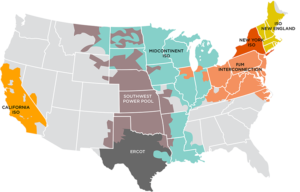
In one form or another, consumers are directly exposed to these complex energy market dynamics. In the wholesale and retail markets there are structures in place to manage and regulate the relationships and financial transactions between the market participants and the consumers. While complicated, they follow similar practices as stock market and financial trading operations between sellers and buyers – in this case the commodity of electricity. The retailer energy provider serves as the broker, or intermediary between the power sources and the consumer. This role has evolved along with the markets so the consumer can actually sell back unused power to the energy market. Bernhard’s Connect® Platform is the enabling technology to make this happen.
Bernhard Connect® is Bernhard’s cloud-based platform for automatic fault detection, measurement and verification, and continuous data collection and archival. The platform provides advanced levels of monitoring and energy management control, pushing the boundaries of existing traditional applications.
New Business Models – New Demand Management Technologies
As the energy markets evolve, new demand management programs are formed to increase customer participation. These programs incentivize customers to shape, shift, and shed load in accordance with a facility’s ability to respond to an event notification and the duration of the event. These range from basic demand response programs where a site develops the capabilities to shed a defined amount of curtailable load, all the way to economic load management programs where hour and day ahead pricing signals inform the building and storage systems with strategies to dynamically control demand. In this way, consumers are paid the same price to shed load as the power plants who deliver electrons.
In this new energy economy, it’s the facilities who have the capability to manage their load through proactive market interaction that benefit. Otherwise, without the necessary enabling technologies, the building operates as a standalone consumer of energy – similar in many respects to a computer not connected to the internet.
Bernhard enables customer participation through Connect by managing the various systems in a facility to lower demand through adjustments to HVAC, lighting and other energy consuming systems, or activating generators and discharging storage batteries.
Connect develops operating strategies to manage demand in context of market conditions – and within the terms and conditions of the power purchasing agreement. This is accomplished by enhancing the customer’s ability to manage their usage that comports with business, operational, and financial rules that are applied under different pricing thresholds. Without Connect, the BAS’s are limited in their ability to interact with energy markets.
When Connect is in place, the customer is ready to engage the new energy markets with confidence and with newfound ability to leverage and negotiate improved power purchasing agreements – because now the customer is able to self-manage risk, and the retail energy supplier has less risk to price.
The customers that have control over their equipment to adjust their demand are going to be the real beneficiaries of the new markets. Those without the ability to monitor and control their buildings will continue to operate blindly and will have to pay the price – whatever it may be.
Dynamic pricing models are coming – depending on which regions your buildings reside, it is either already happening – or coming your way. For example, California’s investor-owned utilities are transitioning to dynamic pricing programs for millions of customers effective April 2023, and utilities around the country have similar plans. Electric rates that more accurately reflect market conditions will help utilities integrate more distributed resources, but many customers have been on fixed rate plans for decades – so this represents changes and new ways for customers to buy and use energy – and this all needs to be supported by solid data to make informed decisions and new technologies to participate.
About the Author:

Leighton’s experience across multiple industries and customer segments enables him to play an integral role in the development and deployment of successful strategic business initiatives and enterprise level projects. Leighton provides expertise and domain knowledge to help clients navigate their way through the highly dynamic intersection of energy markets, emerging technologies and industry players.
He is professionally active on a national level with manufacturers, software developers, systems integrators, facility professionals, government agencies and serves in key roles as owner’s advisor, technical consultant and facilitator providing knowledge of technology and industry trends. In a previous position as VP Strategy for Constellation Energy, Leighton founded the NewEnergy Alliance and formed commercial relationships with over 40 energy technology companies to develop applications and deliver solutions around Constellation’s VirtuWatt Platform, which connected buildings directly to energy markets and Constellation’s trading desk. Leighton is co-developer for this ground-breaking platform.